The Evolution of the Internet

Web 1.0 - the 'read-only' web
Web 2.0 - the 'read-write' web (current mainstream internet)
Web 3.0 - the 'read-write-own' web (the "people's" internet)
What is Web 3.0

Web3, the future internet we’re moving towards, is a decentralized internet. Under Web3, the internet is shared online and governed by the collective “we,” rather than owned by centralized entities. The Web3 world is one that has open-source protocols at its foundation. Web3 is about rearchitecting internet services and products so that they benefit people rather than entities.
Web3 enhances the web we know today by making it decentralized, distributed, open, trustless and permissionless.
It is getting built such that everything would happen in a decentralized distributed way giving no central authority access to control the system. ‘Open’ as it would be open-sourced software built by an open and accessible community of developers and executed in full view of the world. ‘Trustless’ in that the network itself allows participants to interact publicly or privately without a trusted third party. ‘Permissionless’ in that anyone, both users and suppliers,can participate without authorization from a governing body.
This is the future of the internet the term was created by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood in 2014. At this point the internet is not governed by centralized bodies, rather it is shared ad governed by a collective. This period brings about a shift in the internets products so that it benefits the user rather than large co-operatives. It is characterized by a decentralized system and data is not stored in a central database, it is distributed using a peer-to-peer system across different nodes.
Quick Transaction: Because there is no interference of transaction and interaction by a middleman transactions are carried out faster.
Secure: Here your data and privacy are 100% secured, you have total control of your data.
Permissionless: Users and suppliers, can participate without authorization from a governing body.
Trustless: Users can interact with the web without third-party interference.
Decentralized: Web 3.0 is also referred to as a decentralized web, this implies that everything that takes place in Web 3.0 happens without central authority access to control the system.
Web3 applications do not run on a single server, instead, they use blockchain technology and a decentralized network of peer-to-peer nodes. Thereby making it highly secured and difficult to hack.
Features of Web 3.0
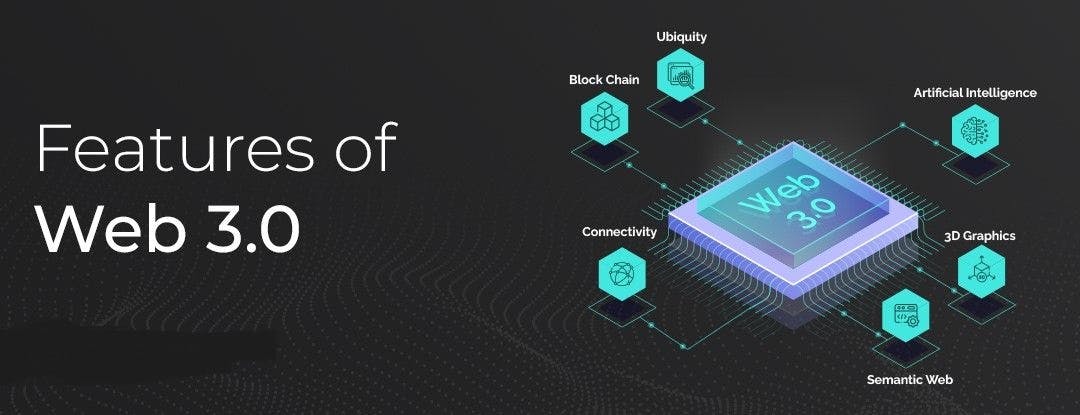
Decentralization: Web 3.0 seeks to eliminate dependency on central authority and intermediaries. Unlike in Web 2.0, where huge tech companies act as the web's core server, users in Web 3.0 can maintain data ownership and management without relying on a centralized authority.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is a distributed ledger that securely stores information by utilizing a peer-to-peer network of computers that interact with one another and smart contracts that are self-executing, thereby eliminating the need for a central authority.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to understand user preferences, behaviours, and interests. This information can be used to tailor content, recommendations, and interactions across different platforms and services, providing users with a more personalized and relevant experience.
Cryptocurrency: Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others would replace government fiat currency.Making bank authorities obsolete and transactions more secure and transparent because cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology.
Semantic Web: The semantic feature of Web 3.0 transforms the internet from a collection of disconnected documents to a vast network of interconnected and meaningful data points. This results in more intelligent applications, better search experiences, and improved interactions between humans and machines.
Edge-computing: It involves the distributed approach of processing and analyzing data closer to the source, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. Data is processed at the "edge" of the network, closer to where it is generated.
Internet of Things (IoT): Integrating physical devices with the internet, allowing them to communicate and exchange data, leading to applications in smart homes, cities, industries, and more.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralized system, data on the blockchain is not governed by a central authority. A Blockchain is a system that assembles and stores structured information and distributes it across the entire network of computer systems connected through peer-to-peer nodes. This assembling of structured information is known as - Digital Ledger. The distribution and storage of data across computer nodes are what make it very secure.
For more information read this blog on Blockchain.
Concept of Node
Blockchain nodes are network stakeholders and their devices are authorized to keep track of the distributed ledger and serve as communication hubs for various network tasks. A Blockchain node's primary job is to confirm the legality of each subsequent batch of network transactions, known as blocks.
Nodes determine whether or not a block of transactions is legitimate and accept or reject it.
Nodes save and store transaction blocks (storing Blockchain transaction history).
This transaction history is broadcast and disseminated by nodes to other nodes that may need to synchronize with the Blockchain ( updates on transaction history are important).
The actual meaning of Decentralization

In blockchain, decentralization refers to the transfer of control and decision-making from a centralized entity (individual, organization, or group thereof) to a distributed network. Decentralized networks strive to reduce the level of trust that participants must place in one another, and deter their ability to exert authority or control over one another in ways that degrade the functionality of the network.
Decentralization is not a new concept. When building a technology solution, three primary network architectures are typically considered: centralized, distributed, and decentralized. While blockchain technologies often make use of decentralized networks, a blockchain application itself cannot be categorized simply as being decentralized or not. Rather, decentralization is a sliding scale and should be applied to all aspects of a blockchain application. By decentralizing the management of and access to resources in an application, greater and fairer service can be achieved. Decentralization typically has some tradeoffs such as lower transaction throughput, but ideally, the tradeoffs are worth the improved stability and service levels they produce.
Benefits of decentralization
- Improves data reconciliation
Companies often exchange data with their partners. This data, in turn, is typically transformed and stored in each party’s data silos, only to resurface when it needs to be passed downstream. Each time the data is transformed, it opens up opportunities for data loss or incorrect data to enter the workstream. By having a decentralized data store, every entity has access to a real-time, shared view of the data.
- Reduces points of weakness
Decentralization can reduce points of weakness in systems where there may be too much reliance on specific actors. These weak points could lead to systemic failures, including failure to provide promised services or inefficient service due to the exhaustion of resources, periodic outages, bottlenecks, lack of sufficient incentives for good service, or corruption.
- Optimizes resource distribution
Decentralization can also help optimize the distribution of resources so that promised services are provided with better performance and consistency, as well as a reduced likelihood of catastrophic failure.
Crypto wallet

In order for a user to interact with the blockchain and store their digital assets, such as cryptocurrency, NFT's, etc - a crypto wallet is needed.
A crypto wallet is a digital wallet that can be accessed on your computer or phone by a unique string of letters and numbers known as your 'private key'. This key should not be shared with anyone!
Wallets can be browser extensions, mobile apps or even hardware wallets.
Each wallet also has a public key.
Anybody can look up your public key and see your transactions, but they cannot access your personal information or interact with your digital assets.
Uses of a crypto wallet
Manage all your digital assets
Control your private keys
Send and receive cryptocurrency
Easy transaction
Access decentralized applications (dApps)
What are private keys
A private key is an alphanumeric code used in cryptography, similar to a password. In cryptocurrency, private keys are used to authorize transactions and prove ownership of a blockchain asset.
What is MetaMask

MetaMask is a software cryptocurrency wallet used to interact with the Ethereum blockchain. It allows users to access their Ethereum wallet through a browser extension or mobile app, which can then be used to interact with decentralized applications. Basically it is an hot Ethereum crypto wallet which you can install as a browser extension or a mobile app. It helps you interact with Ethereum Apps.
Download MetaMask(Highly Recommended!)
Examples of Wallets
Metamask
Coinbase
Phantom
Gas Fees
You will be required to pay Gas Fees for every transaction you make.
This is the 'fee' that the nodes (i.e. the 'miners') receive for validating your transaction and adding it to the blockchain.
The cost of the gas fee depends on which blockchain you're using, and the current user traffic at the time.
If more people are using that particular blockchain network, the miners can increase the gas fee in order to give priority to certain transactions - kind of like Uber Surge where prices go up during peak periods of the day!
Gas fees can range from 0.0001 USD to over 100 USD.
Some blockchain networks such as Polygon have much cheaper gas fees compared to the Ethereum Mainnet, for example.
Crypto Wallet Safety

Check your accounts regularly. It’s imperative that you check your crypto wallet regularly to ensure that your accounts look in order and you can catch suspicious activity quickly. Crypto wallets and digital wallets are unlike the physical ones you carry in your pocket or your bag because when your physical wallet goes missing, you’re likely to notice it quickly. “Phone, keys, wallet” is a mantra most of us sing before walking out the door. Plus, everyone knows the immediate steps to take when a physical wallet goes missing: retrace your steps, put a hold on credit and debit cards, file for a new driver’s license. If you think something is amiss with your wallet, cancel any credit cards linked to your account, change your password immediately and set up two-factor authentication if you haven’t already.
Set up two-factor authentication. Speaking of login security, always make sure you enable two-factor authentication. It is one of the best ways to deter a thief. If your device has biometric authentication, that’s even better. This means that only a scan of your face, voice, or fingerprint will open your accounts.
Know how to identify crypto wallet scams. Watch out for phishers who may be persistent in trying to gain access to your cryptocurrency accounts. If anyone by email, text, phone, or snail mail asks for your private key, ignore the correspondence and go on high alert. Never share your private key with anyone! Phishing attempts often use fear or excitement to trick people into divulging personal information, so don’t fall for messages masquerading as contests or as a crypto company that needs your private key to restore your accounts.
4. Store your seed phrase in a private, safe place.
Setting Up Your First Wallet
Make sure you have the Google Chrome browser.
Download the Coinbase or Metamask Chrome Extension.
Follow the steps to create a new wallet.
Write down the secret recovery phrase and put it in a place that no-one else can access - and where it will be safe.
NOTE: There is no 'helpline' in Web 3 that you can call to recover your wallet! If you lose your secret phrase or if it falls into the wrong hands, you lose your digital assets. So it is your responsibility to always keep it safe!
Pin the wallet to your toolbar in your browser so you can easily access it.
Whenever you would like to interact with a Web 3 website, click 'connect wallet' in the top right of the website and you're set!
Hot VS Cold Wallets
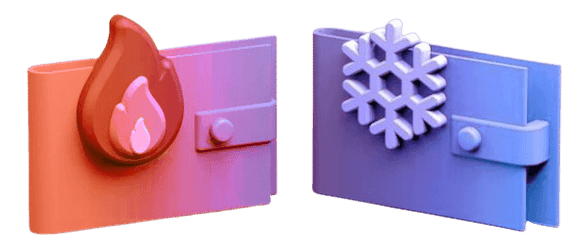
There are two main types of blockchain wallets: hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets are connected to the internet, which makes them more convenient to use. However, they are also more vulnerable to hacking. Cold wallets are not connected to the internet, which makes them more secure. However, they are also less convenient to use.
It is advisable for your crypto wallet to be a hardware wallet (also known as a cold wallet). This is a device that looks like a USB stick that you can store safely offline.
Hot wallets are online wallets that are easily accessible to hackers on the internet. They are convenient for transactions but are also less secure.
Examples of hardware wallets are: Ledger and Trezor.
Hot wallets are generally free, whereas cold wallets require you to purchase them.
How Does Web 3 Work?
Basically, data is encrypted and stored across multiple nodes operated by multiple users around the world.
(In Web 2.0, data is stored on cloud servers such as those owned by Google, Amazon, etc.)
Nodes are computers where users share their computer disk space in exchange for a fee.
These nodes make up the blockchain network.
Web 3.0 Applications

Uniswap
Aave
OpenSea
Decentraland
Steemit
Storj
Concept of ETH
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that establishes a peer-to-peer network that securely executes and verifies application code, called smart contracts. Smart contracts allow participants to transact with each other without a trusted central authority.
Ethereum has a native currency called "Ether", or "Eth". This token is required to pay transaction fees for transactions done on the Ethereum network.

Benefits of building on Ethereum
Ethereum offers an extremely flexible platform on which to build decentralized applications using the native Solidity scripting language and Ethereum Virtual Machine. Decentralized application developers who deploy smart contracts on Ethereum benefit from the rich ecosystem of developer tooling and established best practices that have come with the maturity of the protocol. This maturity also extends into the quality of user-experience for the average user of Ethereum applications, with wallets like MetaMask, Argent, Rainbow and more offering simple interfaces through which to interact with the Ethereum blockchain and smart contracts deployed there. Ethereum’s large user base encourages developers to deploy their applications on the network, which further reinforces Ethereum as the primary home for decentralized applications like DeFi and NFTs. In the future, the backward-compatible Ethereum 2.0 protocol, currently under development, will provide a more scalable network on which to build decentralized applications that require higher transaction throughput.
Concept of Seed phrase
A seed phrase is a series of words generated by your cryptocurrency wallet that give you access to the crypto associated with that wallet. Think of a wallet as being similar to a password manager for crypto, and the seed phrase as being like the master password.
The future of Web 3.0

The future of the web holds exciting possibilities with Web 3.0 evolving with its different amazing features, as stated earlier. Users will experience a more user-centric, interconnected, and dynamic digital web.
Some technologies and concepts associated with Web 3.0, such as blockchain, decentralized applications (DApps), and digital ownership through NFTs, have gained prominence.
While progress is being made towards these goals, the complete realization of Web 3.0's vision may take some time, as it requires widespread adoption of new technologies, changes in internet infrastructure, and shifts in user behaviours.
References
https://www.theproduct.house/learn/web3-academy
That's all for this blog, I hope you will learn something new. And feel free to share your thoughts and feedback, Thanks for reading.
Feel free to reach out to me 👀
Twitter 🖱
LinkedIn 🖱
Github 🖱