Table of contents
- Introduction to Polygon
- Sidechain Network
- Polygon PoS
- Polygon Plasma
- ZK Rollups
- Optimistic Rollups
- The Ethereum Layer
- Uses and advantage
- Advantages
- Disadvantage
- How is Polygon Different From Ethereum?
- What are Polygon NFTs?
- Getting Started With Polygon NFTs
- Connecting to Polygon
- Connect Manually
- Connect Automatically
- What is a Polygon (MATIC)?
Introduction to Polygon
Polygon (formerly Matic Network) is a blockchain platform that aims to create a multi-chain blockchain system compatible with Ethereum. As with Ethereum, it uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism for processing transactions on-chain. Polygon's native token is named MATIC. Matic is an ERC-20 token, allowing for compatibility with other Ethereum cryptocurrencies. In simple words, Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum. It is both a framework and a network of sidechains previously known as the MATIC network.

The Polygon framework allows you to create a personalized sidechain with a set of customized properties. You get the building blocks you need to create your own chain while maintaining power over how exactly you want to set it all up. The SDK is written in Go and allows a proficient developer to quickly wire together components until you have a working node/client that you can deploy. Everything, especially on a lower level, is taken care of for you. You don’t need to deal with message passing between chains or syncing states; the SDK already has that implemented for you.
Sidechain Network
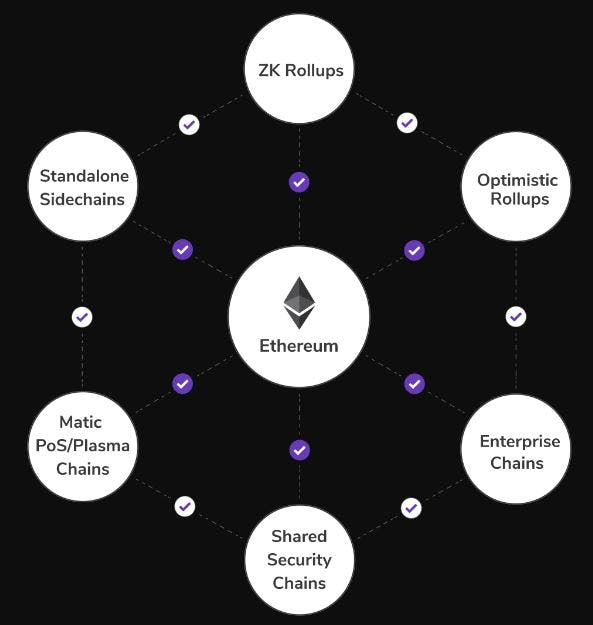
There are five components of the network are essential to its operational readiness:
Polygon PoS
Polygon Plasma
ZK Rollups
Optimistic Rollups
The Ethereum Layer
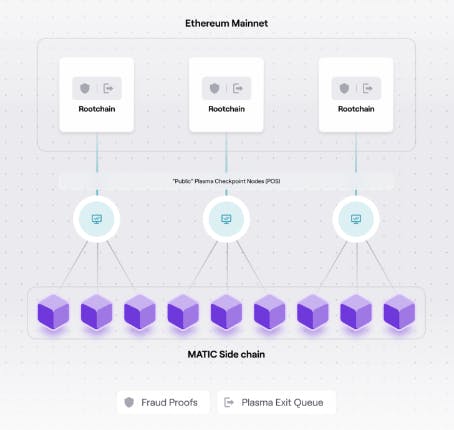
Polygon PoS
Polygon PoS adds an overall Proof-of-Stake consensus protocol to Polygon’s network of sidechains.
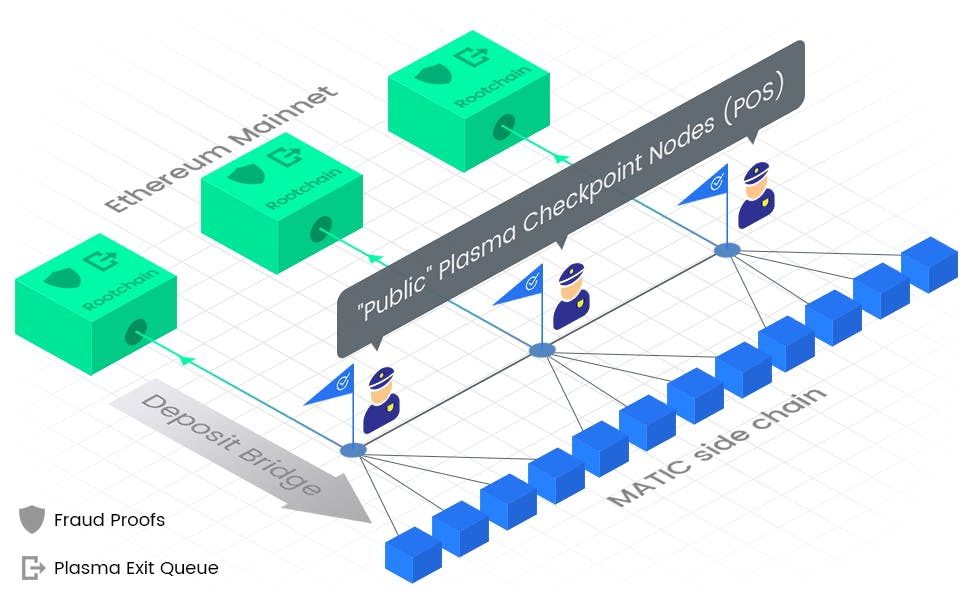
Polygon Plasma
Plasma is a scaling solution to move assets between the root chain and its child chains through Plasma bridges.
ZK Rollups
ZK Rollups are an alternative scaling solution where many transactions are bundled off-chain into a single transaction. It uses zero-knowledge proofs for the final record on the Ethereum main chain.
Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic Rollups run on top of Ethereum to enable near-instant transactions with the help of so-called fraud-proofs.
The Ethereum Layer
At some point, Polygon needs to interact with Ethereum. This is realized with a set of smart contracts deployed to Ethereum. They enable the communication between Ethereum and all Polygon chains, take care of staking and transaction finality, and the overall communication between the two.
Uses and advantage
Users interacting with Polygon usually only see Polygon as a whole blockchain, and the underlying architecture is not important for the everyday user. Any Ethereum-compatible web wallet can connect to Polygon, acquire funds (MATIC), and interact with dApps deployed somewhere within the network. OpenSea, for example, has allowed minting and trading NFTs on Polygon for a while now. You only need to switch the chain your wallet is connected to, and everything works. The UX is not different from Ethereum, which makes Polygon also an excellent solution usability-wise. Overall, the space might still have a UX problem, but it doesn’t get any worse by choosing Polygon.
The next time you open Uniswap, go to OpenSea or even want to deploy a smart contract, think about Polygon for a moment. It might be a valid alternative to deploying on Ethereum, at least for now, until Ethereum 2.0 finally hits and hopefully solves many of the original issues. And even after that, Polygon offers a unique approach to scaling and community building with custom sidechains that are fully interoperable with Ethereum.
Advantages
Low Fees: Through using PoS and rollups, transaction fees on Polygon are comparatively lower than other networks, like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Fast Transaction Times: Polygon gives users multiple options to move digital assets across the network. Rollups can bundle thousands of transactions into one succinct package. The PoS protocol is a relatively faster way to validate transactions (when compared to methods like PoW). This combination of scaling solutions leads to overall faster transaction times on the network.
Designed to Scale: Polygon was designed from the ground up to scale and improve upon Ethereum. Each sidechain performs a unique function. Developers are not tied to building on any one particular chain. Users can transact on whatever chain they please. Polygon is not reliant on a one-size-fits-all solution for growth, allowing users to experiment and choose which solution works best for their needs.
Staking: Users can also earn rewards by participating in securing the network. Validators are the more active participants, taking part in the consensus group work. Delegators typically take a more passive approach to staking by delegating their stake to a validator for a fee.
Disadvantage
Not Autonomous: Some investors could be turned off by Polygon’s deep connection to Ethereum. It appears the network's utility relies almost entirely on Ethereum's continued growth. While Ethereum is one of the largest crypto networks in existence, if it fails, then it’s highly likely that Polygon will also fail.
Limited MATIC Use Cases: Within the network, MATIC functions as a utility token. Yet its utility ends anywhere outside of Polygon. It’s also an ERC-20 token, which exclusively limits its use cases to Ethereum and other related networks.
Slow Withdrawal Times: While the PoS Chain is fairly efficient, Polygon’s Plasma Chain has slow withdrawal times built into its design. Given the additional security measures used here, it may take users exiting Ethereum up to a week to transfer assets to Polygon. The PoS Chain is a faster alternative.
How is Polygon Different From Ethereum?

Polygon and Ethereum were formed from two different ideas. Ethereum founder, Vitalik Buterin seeks to create a secure, scalable network that does not compromise its decentralization. Polygon founders seek to be the premier scaling platform for Ethereum. With two differing goals arise two networks that are structurally unique.
When Ethereum was a Proof of Work (PoW) network with remarkably high traffic, it encountered various issues that impeded its growth and usability. Transaction speeds were particularly slow during busy times. Gas fees would often skyrocket during these periods, which made it remarkably expensive for the average investor to participate in the network.
Polygon sought to solve these problems through the use of multiple sidechains, a PoS consensus model, and rollups. Ethereum decided to take their chances at solving these problems internally, gradually rolling out updates across the network.
While there is some overlap in how both networks attempt to solve the scalability trilemma, Ethereum will always be a standalone project. Polygon can only maintain its utility as long as people remain interested in using Ethereum.
In saying this, the two networks equally benefit from a synergetic relationship. Polygon and Ethereum work alongside one another, with both their future success reliant on the continued success of the other.
What are Polygon NFTs?
Polygon NFTs are non-fungible tokens that were either minted on the Polygon blockchain or bridged from another chain to the Polygon blockchain. Regardless of their provenance, all Polygon NFTs benefit from the network’s low gas fees and quick transaction times relative to the Ethereum mainnet.
The Polygon NFT ecosystem is home to teams such as y00ts and Hell Cats, marketplaces like OpenSea and Magic Eden, gaming projects like Benji Bananas and Arc8, as well as countless other dApps. Over 843 million NFTs have been minted on the Polygon blockchain to date, with total NFT volume surpassing $16 billion.
Getting Started With Polygon NFTs
First things first, you will need a wallet and some Polygon’s native MATIC tokens. MetaMask is one of the most popular wallets, but there are lots of other options. If you don’t yet have a MetaMask wallet, here is a step-by-step guide to getting one.
MetaMask is the most popular cryptocurrency wallet app and browser extension used to access the Web3 universe. In just a few simple steps, you can unlock this powerful tool and begin exploring the Polygon ecosystem.
MetaMask is available for download and installation on a variety of platforms with two main flavors: desktop browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Brave, and Microsoft Edge) and mobile (iOS and Android). Get the one that’s right for you from the official website.
After you've downloaded and installed the extension or app, launch it and click 'Get Started.'
If this is your first time creating a MetaMask wallet, click the 'Create a Wallet' button. You can also use a Secret Recovery Phrase to import your existing MetaMask wallet.
In order to improve MetaMask, you have the option of sharing anonymous usage data with MetaMask. This can be turned off at any time by going to Settings and unchecking the box.
Create a password. MetaMask will then share with you your Secret Recovery Phrase, which serves as the master key to our wallet and will let you regain access to your account if you lose the password.
Click 'Next' to see your 12-word seed phrase. Verify it by selecting each word in the correct sequence. Click "Confirm."
We recommend that users keep their seed phrase offline and in a secure location. Sharing it with someone is the same as handing over your wallet.
You've now completed the setup process for your MetaMask wallet. Click 'All Done.'

Connecting to Polygon
Connect Manually
On mobile, click the hamburger icon in the top left, go to Settings and down to Networks. On the browser, the network selection window is usually in the top right.
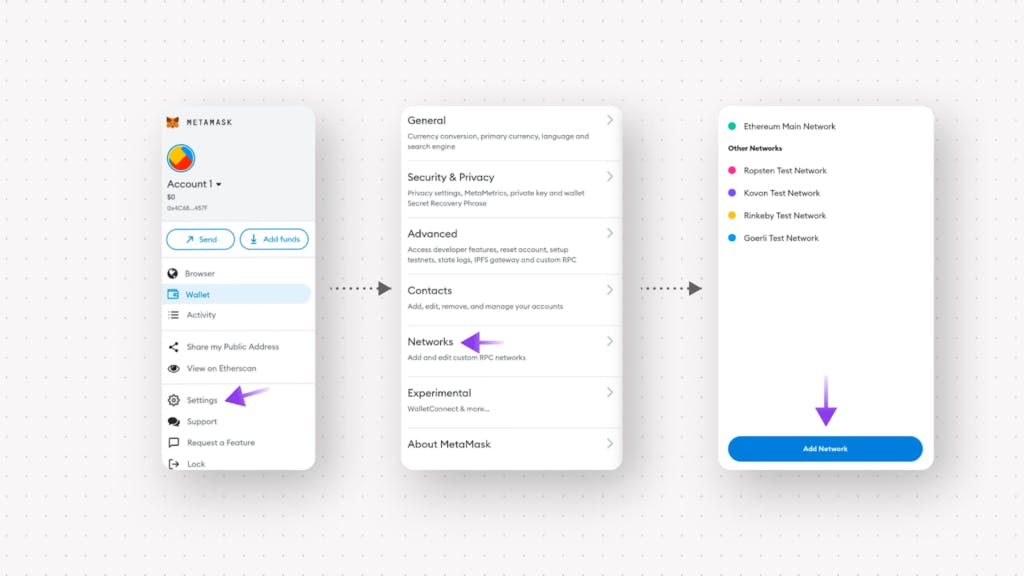
On the desktop, simply click the 'Add network' button under the drop-down network menu at the top right corner. Refer to the below screenshot:
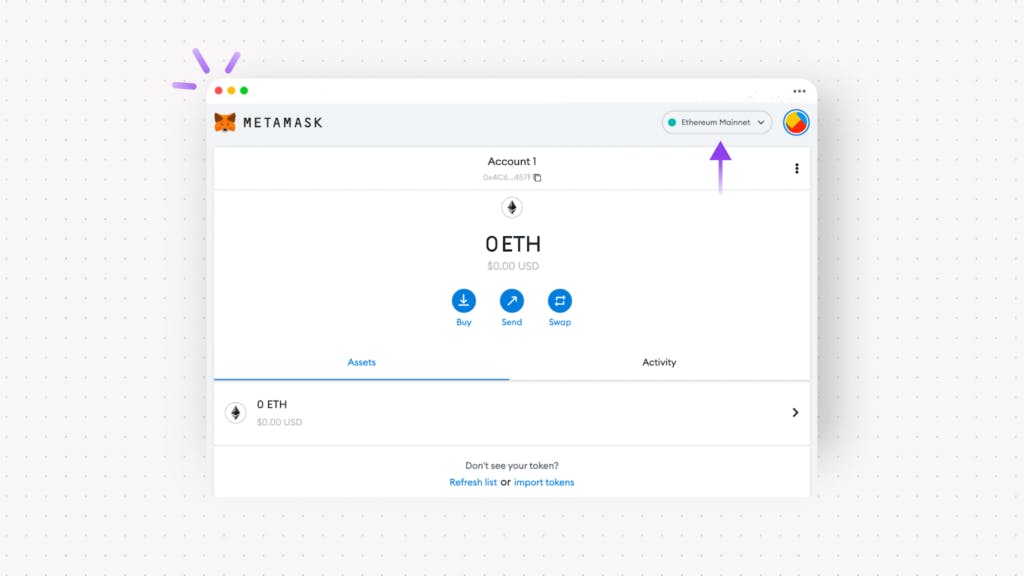
- Click 'Add network' and fill in the following information:
Network Name: Polygon Mainnet
New RPC URL: polygon-rpc.com
Chain ID: 137
Currency Symbol: MATIC
Block Explorer URL: polygonscan.com
Click “Save.”
Welcome to Polygon!
Connect Automatically
On polygonscan, go to the bottom of the page and click the "Add Polygon Network" button.
A MetaMask Notification will appear. Click “Approve” to proceed.
In the network dropdown list, you'll be taken straight to Polygon's Mainnet.
Done!
What is a Polygon (MATIC)?
Polygon (MATIC) is a Layer 2 open-source protocol built by a decentralized team of contributors from all around the world, created as a framework for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks.
Polygon is quickly becoming Ethereum’s Internet of blockchain. Polygon offers security as a service, custom modules, interoperability, and one-click deployment of preset blockchains.
With Polygon, any project can have its own dedicated version of Ethereum while maintaining a direct connection to the growing Ethereum Blockchain. As the fastest-growing Ethereum scaling platform in development, Polygon believes Web3 should be easily accessible for everyone.
With billions of transactions recorded, hundreds of million unique wallets, and three million monthly active users, Polygon is the most proven scaling solution in web3 and the best way to launch a web3 project that’s ready for a global audience.
How Does Polygon Work
Polygon utilizes Proof of Stake to scale the development of applications on Polygon Network. This helps Polygon achieve unprecedented transaction speed and cost savings by utilizing side chains for transaction processing.
At the same time, Proof of Stake ensures asset security with Plasma bridging frameworks and a decentralized network of transaction validators. Transaction speeds of up to 65,000 transactions per second mean significantly faster performance than Ethereum’s ability to process only 15 transactions per second.
By storing just a small portion of compressed data on the blockchain, the efficiency and throughput of the Polygon Network are built to complement and scale with the Ethereum Network.
Decentralized applications (dApps) built using Polygon are held to the highest standards of security and scalability. Polygon strives to solve the scalability and usability issues without compromising decentralization.
Before Polygon, the user experience for many dApps built on Ethereum was lacking greatly. This is due to the limitations of Ethereum as the need for new applications began to grow.
Polygon solved many of these issues plaguing the growing pains associated with many new applications. The ability to have near-instant transactions meant a far better experience for Ethereum users. Today we can thank Polygon for enabling over 1,500 amazing Decentralized Applications in the Ethereum Ecosystem
MATIC vs Polygon
Before the project changed its name in February 2021, Polygon was known as Matic Network. The Matic network had one primary offering: plasma sidechains.
Plasma chains are a bit like side chains, except they offer greater security in exchange for convenience. Unlike sidechains, Plasma chains publish their “root” on Ethereum layer 1 and function based on the assumption that its consensus mechanism can fail. This design affords greater security but while rendering these chains unable to run complex operations.

After the project expanded, Polygon opted to keep the ticker MATIC for its native token. Thus, the Matic network became Polygon. This name change and subsequent rebranding may generate some confusion, but they are the same project. Polygon is the new umbrella for multiple projects including the Matic network.
What is the Polygon MATIC token used for?
MATIC is Polygon’s native cryptocurrency token. Polygon plasma chains run on the PoS consensus mechanism. MATIC will be used to pay for all transactions on the plasma chains. Therefore, the more projects that use Polygon as a scaling solution, the greater the demand for MATIC.
In addition, MATIC serves as a governance token by granting holders the right to vote on which of the several scaling solutions planned should actually be rolled out.
Why is Polygon good for Ethereum
Polygon isn’t in competition with Ethereum. If anything, it’s reliant on Ethereum and vice versa. Polygon’s mission is to leverage the Polygon network in order to create an infrastructure that can handle the mass adoption of Ethereum. Consequently, Polygon is more dependent on Ethereum than Ethereum is on Polygon. This is expected since Polygon is built on top of its blockchain.
The main disadvantage is that switching to Polygon for speed may dilute the value gained by Ethereum. Value dilution might actually hinder Ethereum’s direct user growth in certain locations.
Polygon improves Ethereum and, thus, more people will use the Ethereum blockchain. With more users locking their capital in the Ethereum blockchain freely, its value will rise, despite the potential for stealing total value locked (TVL) away from Ethereum.
🚩 https://university.polygon.technology/
🚩 https://polygon.technology/blog
🚩 https://wiki.polygon.technology/docs/home/architecture/polygon-architecture/
🚩 https://polygon.technology/blog/polygon-2-0-protocol-vision-and-architecture
That's all for this blog, I hope you will learn something new. And feel free to share your thoughts and feedback, Thanks for reading.
Feel free to reach out to me 👀
Twitter 🖱
LinkedIn 🖱
Github 🖱