What is Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a simulated experience that employs pose tracking and 3D near-eye displays to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video games), education (such as medical or military training) and business (such as virtual meetings).

In other words, Virtual Reality (VR) is a computer-generated environment with scenes and objects that appear to be real, making the user feel they are immersed in their surroundings.
How VR is different from XR/AR

Extended Reality (XR)
Extended reality (XR) is a term that encompasses real and virtual environments that are generated by wearable devices or computer technology to provide an immersive experience. It can also be described as a collection of all immersive technologies that combine real and virtual worlds.
Augmented reality (AR)
Augmented reality (AR) is the real-time use of information in the form of text, graphics, audio and other virtual enhancements integrated with real-world objects. It is this "real world" element that differentiates AR from virtual reality.
For example, think of Pokémon Go, where users are searching in their real-life neighborhoods for animated characters that pop up on their phone or tablet.
Types of VR
To make it simpler, This will categorize the features of VR into three

Immersion
Immersion is also known as presence, refers to the degree of reality that the viewer exists in the virtual environment as the protagonist. Viewers can put themselves in a virtual environment and become a part of the virtual environment by wearing interactive devices such as helmet-mounted displays and data gloves.

The interaction between the viewer and various objects in the virtual environment makes the viewer feel like they are just like in the real world. The viewers’ brain tricks themselves with what they are seeing and hearing from the VR head-mounted displays or a VR headset giving them an immersion feeling and thinking that what they are experiencing feels real.
Non Immersion

This technology provides a computer-generated environment but allows the user to stay aware of and keep control of their physical environment. Non-immersive virtual reality systems rely on a computer or video game console, display, and input devices like keyboards, mice, and controllers.
Interaction

Interaction refers to the user’s degree of maneuverability of objects in the simulated environment and the natural degree of feedback from the real environment. The human-computer interaction in VR technology is natural-like interaction. There are two types of interactions which are the three-degree-freedom (3DoF) interaction and the six-degree-freedom (6DoF) interaction. Normally, 3DoF is where a viewer can view a 360° image or video using a VR headset and move their head side to side to explore around; whilst the 6DoF requires a powerful gaming laptop or computer to process information to play and interact with using extra accessories such as sensors, data gloves and other sensing devices. The device adjusts the image and audio presented by the system according to the movement of the viewer’s head, hands, eyes, language and body. Viewers can inspect or manipulate objects in the virtual environment through natural skills such as their own language, body movements or actions.
Imagination
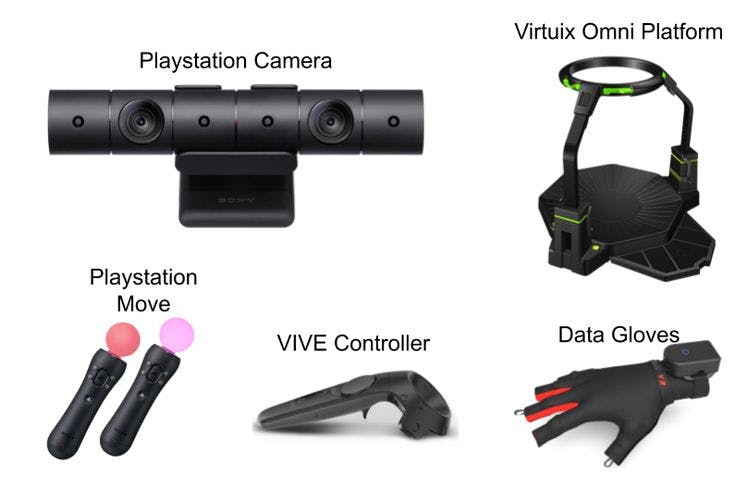

Since the VR system is equipped with sensing and responsive devices for sight, hearing, touch, and kinesthetics, viewers can obtain various perceptions such as vision, hearing, touch, and kinaesthesia through human-computer interaction in the virtual environment to achieve an immersive experience. The research and development of VR are to expand human cognition and perception capabilities and establish a harmonious human-machine environment. VR technology is a perfect combination of humans and technology that is a product of computer graphics and human-computer interaction technology. Humans occupy a very important position in the entire system. Using the means of VR technology, we can get an “immersive” experience of the research object and environment, thereby enhancing the breadth and depth of human cognition, and broadening the “cognition space” and “method space” for humans to understand the objective world. Ultimately achieving a more essential reflection of the essence of the objective world.
Immersive VR System
The immersive VR system uses various interactive devices such as head-mounted displays and data gloves to seal the viewer’s vision, hearing and other senses and use interactive devices to operate and control the virtual environment so the viewer truly becomes a participant in the VR system creating a sense of being immersed and fully engaged.
What is Mixed Reality

Mixed reality is a combination of both AR & VR, where one can interact with the digital as well as the real world simultaneously. Users can visualize their surroundings in special MR devices. These MR devices are much more powerful than VR, and costly too! But these devices give you the power to interact with the surroundings digitally. For example, putting on an MR device will give you a view of your entire surroundings. You can do whatever you want, throw a ball, close the windows, etc which will be digitally in your MR headset, but in actual reality, things will remain as they are. Many companies are investing a huge amount of money for deeper research in this field of reality.
In a nutshell, using Extended Reality(XR), people can visit places virtually, feel the same as they are present at that place, and interact with other individuals on XR. Thus, it is a combination of all three AR, VR & MR.
How Virtual Reality Works
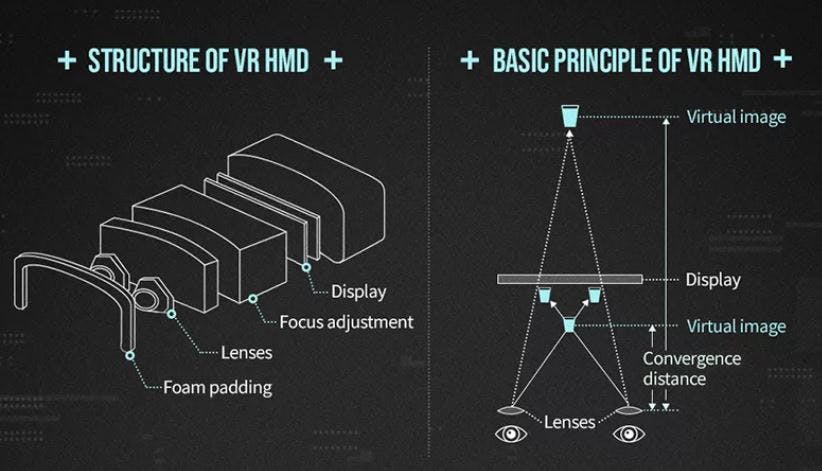
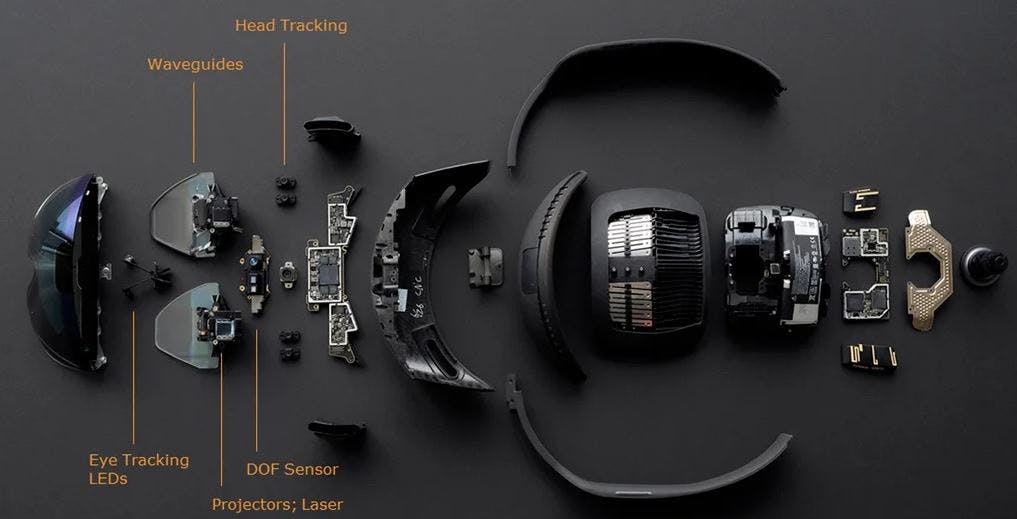
For virtual reality to work, there must be an optical system in a head-mounted display that will project an image on a display in front of your eyes.
In this optical system, an HMD includes light sources (display), receivers (eyes), and optical elements (lenses).
The light sources in an HMD are microdisplays, such as organic light emitting diodes (OLED) or liquid crystal displays (LCD). A binocular HMD typically has two displays that provide separate images for each eye and generate 3D perception through stereoscopy. In a holographic HMD, the light source is modulated coherent light from a spatial light modulator (SLM).
The receivers in HMDs are the eyes of the user.
The optical elements collect light from the source and generate renderings of a 3D virtual world. An ideal VR HMD must be able to provide a high-resolution image within a large field of view (FOV) while supporting accommodation cues for 3D perception and have a large eyebox (exit pupil) with a compact form factor
Headsets — The Basics
The whole point of VR is to immerse yourself in a new world. However, other than the VR headset, there are also many other parts necessary for VR to actually work. VR headsets like Playstation VR and Oculus Rift are called head mounted displays, which means that the screen is mounted to your face. Wherever you move your head, the screen follows you.
For certain VR headsets like the HTC Vive and the Oculus Rift, a console or computer is needed for the headsets to work. Video is sent from the console or the computer to the VR headset. For other headsets like the Google Daydream and the Samsung Gear VR, a smartphone has to be slotted into the headset, and the video plays from the phone.

VR headsets either use two LCD displays (one per eye) or two feeds sent to one display. Headsets also have lenses placed between your eyes and the screen, which are used to focus and reshape the picture for each eye. They create a stereoscopic 3D image by angling the two 2D images. This is because the lenses mimic how each of our two eyes sees the world very slightly differently.

VR headsets also need to have a minimum frame rate of at least 60 frames per second in order for the user to not feel sick. Current VR headsets are able to go way beyond this, with Oculus and the HTC Vive at 90 frames per second and PlayStation VR at 120 frames per second.
Head Tracking
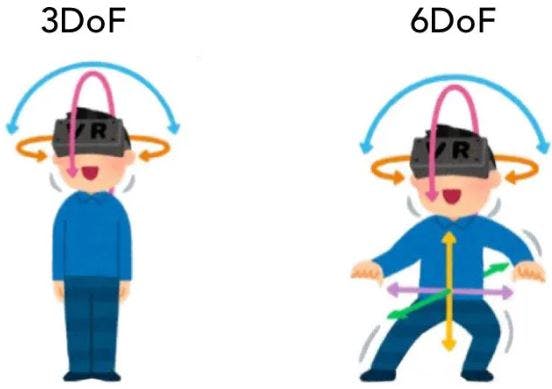
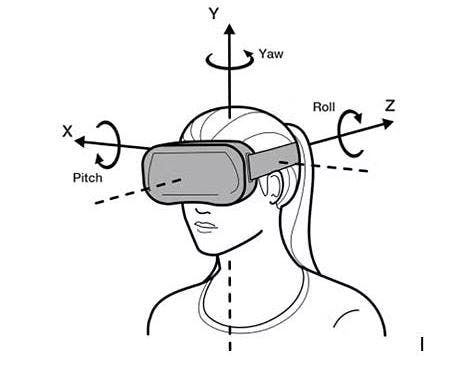
For VR to work properly, when you move your head up and down or side to side or tilt your hear, the picture has to move properly with your head. Headsets use a system called six degrees of freedom (6DoF), which looks at your head’s position in terms of the X, Y, and Z axis to measure head movements.
There are a couple of different components use in a head-tracking system, including a gyroscope, accelerometer, and a magnetometer. The PlayStation VR also uses 9 LEDs around the headset, which are used to provide 360 degree head tracking by using an external camera that monitors these signals.
Motion Tracking
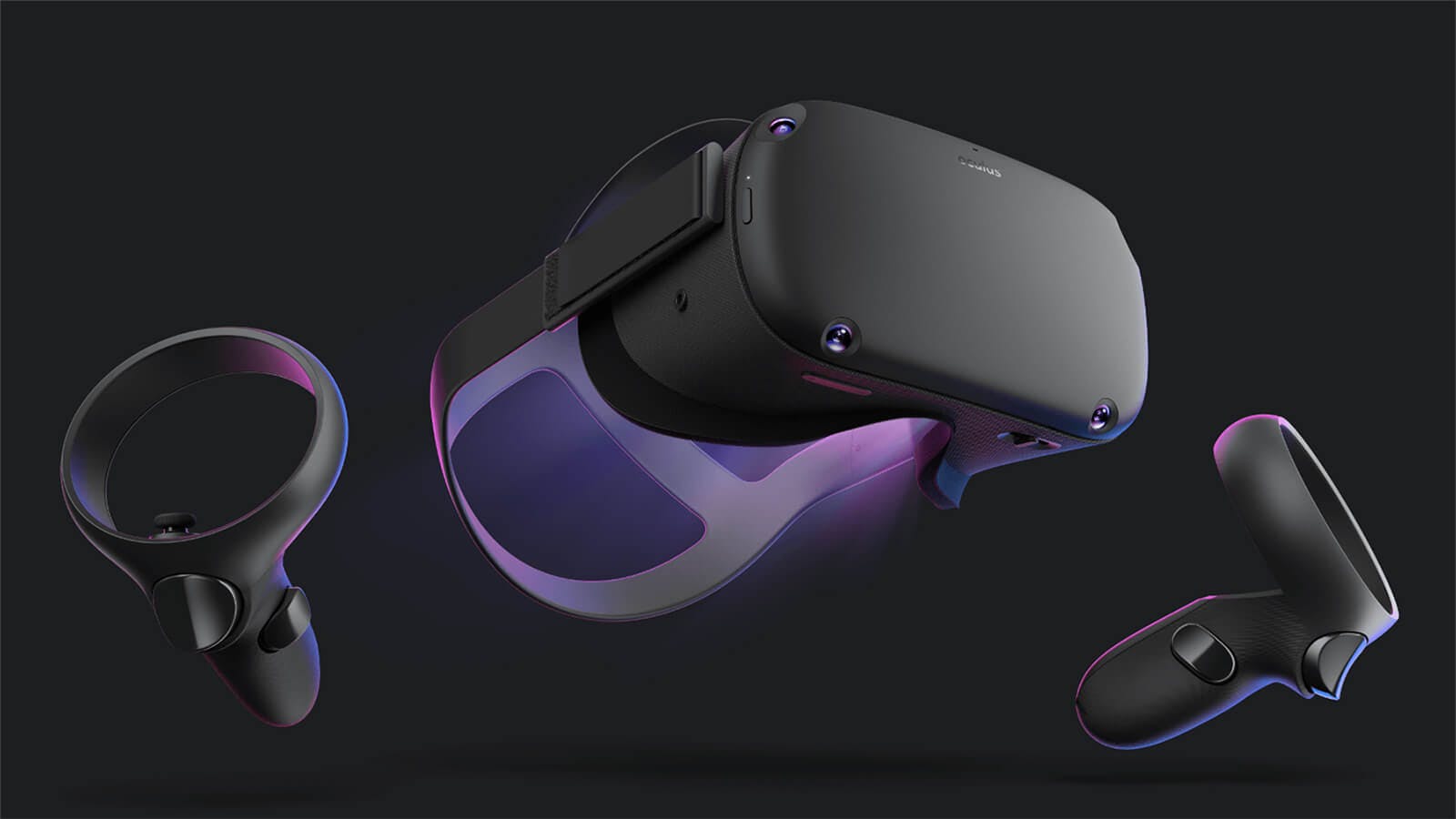

VR headsets like the Oculus Rift and the HTC Vive have a set of wireless controllers that are used to make you feel like you are controlling what is happening in your VR simulation. There are certain buttons on the controller as well as a lot of sensors to detect gestures such as pointing and waving. Different input methods include voice controls, smart gloves, and even treadmills, which allow you to simulate walking around in a VR environment.
Dev Tools for Virtual Reality
Unity

Unity is famous for game development, however, it helps you to build VR solutions for many other sectors too. E.g., you can create VR solutions for automotive, transportation, manufacturing, media & entertainment, engineering, construction, etc. with Unity.
Google VR for Everyone

Google offers a wide range of VR development tools, and you can use them to create an immersive VR experience for your stakeholders. You can access these tools on the Google VR developer site.
Unreal Engine 4 (UE4)

Unreal Engine 4 (UE4) offers a powerful set of VR development tools. With UE4, you can build VR apps that will work on a variety of VR platforms, e.g., Oculus, Sony, Samsung Gear VR, Android, iOS, Google VR, etc.
Blender

Blender 3D is a powerful and popular open-source software for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. In recent years, Blender has also become a popular tool for creating virtual reality (VR) experiences, particularly in the field of architecture.
3ds Max

3ds Max is a popular 3D modeling and rendering software from Autodesk and 3ds Max is used to model, animate, and render detailed 3D characters, photorealistic designs, and complex scenes for film and TV, games, and design visualization projects.
SketchUp Studio

SketchUp Studio is a powerful 3D modeling tool focused on the construction industry and architecture, and you can use it for virtual reality app development. It’s useful for use cases like architecture, commercial interior design, landscape architecture, residential construction, 3D printing, and urban planning.
Uses of Virtual Reality

- Healthcare
The technology is also being used in cognitive behavior therapy where patients with phobias and anxieties work through their problems in a controlled environment.
- Entertainment
VR is being introduced to cinemas and theme parks to simulate movie-like adventures and let people experience their favorite cinematographic masterpieces.
- Automotive
Virtual reality is widely used in the development of smart cars that will flood the market in the future. Cars learn how to drive, turn, and stop using artificial intelligence (AR) and virtual reality.
- Education
Lots of industry can provide professional training to their employees. But for younger students, VR is part of educational games, field trips, and in general experiencing the world.
- Space & Military
VR enables trainees to go through preparation with minimal risks and even helps soldiers suffering from battlefield trauma to overcome these conditions and prepare for new or unexpected situations.
- Social Science and Psychology
Much of this industry relies on VR so that a patient can embody someone else and imagine reality from a different perspective or worldview. Immersive environments can leave positive impacts on future social interactions.
Major Challenges

VR in education is the lack of effective social interaction and collaboration features. VR can enable learners and educators to interact and collaborate with each other and with virtual characters or agents in various ways. However, VR also poses technical and social challenges, such as latency, bandwidth, synchronization, communication, coordination, and trust. Social interaction and collaboration are essential for learning, especially for developing social and emotional skills, such as empathy, communication, and teamwork. Therefore, educators and designers need to enhance and facilitate social interaction and collaboration in VR for education.
Another drawback of VR in education is the ethical and legal implications of VR use and development. VR can raise various ethical and legal issues, such as privacy, security, consent, ownership, copyright, accessibility, diversity, inclusion, and accountability. VR can also affect the psychological, physical, and social well-being of users and stakeholders. These issues require careful consideration and regulation to ensure the responsible and beneficial use of VR for education. Therefore, educators and policymakers need to establish and follow ethical and legal guidelines and standards for VR for education.
The Future of VR

The future of virtual reality is increasingly leaning towards multisensory experiences. It's not just about what users can see; it's about what they can touch, smell, and even taste. The more realistic the virtual world, the more immersive and captivating the experience for the user.
VR is going to play such a huge role in our lives over the next couple of years, and it will change the way we live altogether. VR is a technology that can impact every single industry, from healthcare to space, to construction, to travel. This technology is going to be extremely powerful very soon.
VR aims to create a sensory experience for the user, sometimes including sight, touch, hearing, smell, or even taste. The industry is growing at a fast pace, with the global VR market size projected to increase from less than 12 billion U.S. dollars in 2022 to more than 22 billion U.S. dollars by 2025
Reference
🚩 https://youtu.be/wJzHjk1QT3E?si=qFOTYq-mvEU81mKt
🚩 https://youtu.be/04AMaTsXFJU?si=IGU6cVvcWAy-f3oV
🚩 https://youtu.be/WzfDo2Wpxks?si=cSJxnqdSkmJGk_yo
🚩 https://youtu.be/XLP4YTpUpBI?si=yDWv1kVnXtTZReDt
That's all for this blog, I hope you will learn something new. And feel free to share your thoughts and feedback, Thanks for reading.
Feel free to reach out to me 👀
Twitter 🖱
LinkedIn 🖱
Github 🖱