What is Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is the real-time use of information in the form of text, graphics, audio and other virtual enhancements integrated with real-world objects. It is this "real world" element that differentiates AR from virtual reality.

For example, think of Pokémon Go, where users are searching in their real-life neighborhoods for animated characters that pop up on their phone or tablet.
Types of augmented reality
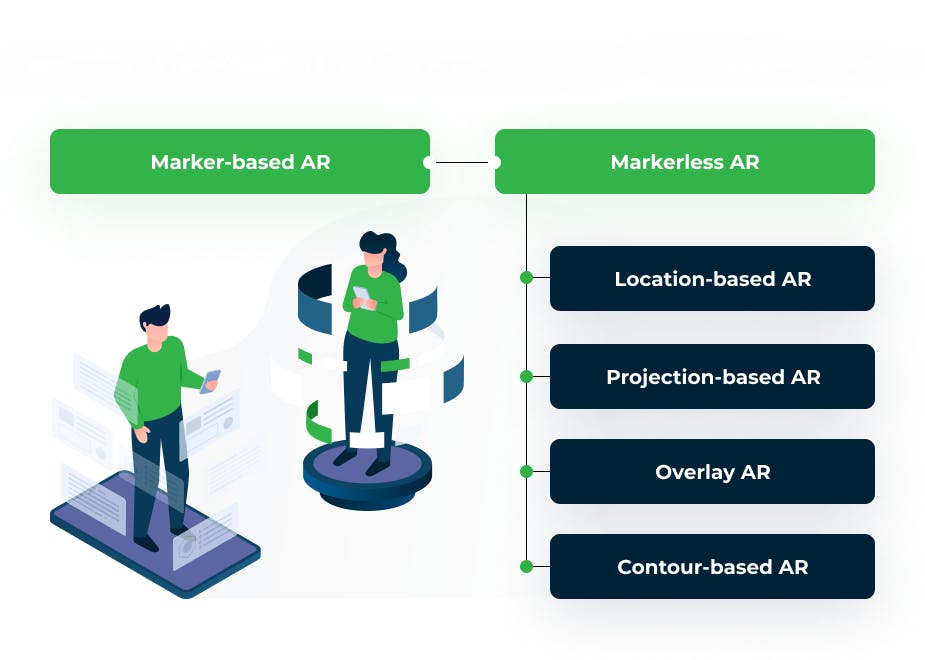
Marker-based AR is created using image recognition to identify objects already programmed into your AR device or application. When placing objects in view as points of reference, they can help your AR device determine the position and orientation of the camera. This is generally achieved by switching your camera to grayscale and detecting a marker to compare that marker with all the others in its information bank. Once your device finds a match, it uses that data to mathematically determine the pose and place the AR image in the right spot.
Marker-less AR is more complex as there’s no point in which your device will focus on. Because of this, your device must recognize items as they appear in view. Using a recognition algorithm, the device will look for colors, patterns, and similar features to determine what that object is and then, using time, accelerometer, GPS, and compass information, it will orient itself and use a camera to overlay an image of whatever you’d like within your real-world surroundings.
How AR is different from XR/VR
Extended Reality (XR)
Extended reality (XR) is a term that encompasses real and virtual environments that are generated by wearable devices or computer technology to provide an immersive experience. It can also be described as a collection of all immersive technologies that combine real and virtual worlds.

Virtual Reality (VR)
This immersive technology employs a head-mounted display (HMD) to provide an immersive expression through a simulation (or simulated environment). The simulated digital environment makes users feel as if they are there.
What is Mixed Reality
Mixed reality is a combination of both AR & VR, where one can interact with the digital as well as the real world simultaneously. Users can visualize their surroundings in special MR devices. These MR devices are much more powerful than VR, and costly too! But these devices give you the power to interact with the surroundings digitally. For example, putting on an MR device will give you a view of your entire surroundings. You can do whatever you want, throw a ball, close the windows, etc which will be digitally in your MR headset, but in actual reality, things will remain as they are. Many companies are investing a huge amount of money for deeper research in this field of reality.

In a nutshell, using Extended Reality(XR), people can visit places virtually, feel the same as they are present at that place, and interact with other individuals on XR. Thus, it is a combination of all three AR, VR & MR.
How Augmented Reality Works
Augmented reality can be delivered in a variety of formats, including within smartphones, tablets and glasses. AR delivered through contact lenses is also being developed. The technology requires hardware components, such as a processor, sensors, a display and input devices. Mobile devices already typically have this hardware available, with sensors including cameras, accelerometers, Global Positioning System (GPS) and solid-state compasses. This helps make AR more accessible to the everyday user. A GPS is used to pinpoint the user's location, and its compass is used to detect device orientation, for example.
Sophisticated AR programs used by the military for training can also include machine vision, object recognition and gesture recognition. AR can be computationally intensive, so if a device lacks processing power, data processing can be offloaded to a different machine.
Augmented reality apps are written in special 3D programs that enable developers to tie animation or contextual digital information in the computer program to an augmented reality marker in the real world. When a computing device's AR app or browser plugin receives digital information from a known marker, it begins to execute the marker's code and layer the correct image or images.
Generally, Augmented reality creates an immersive experience for all its users. Though the most common AR forms are through glasses or a camera lens, interest in AR is growing, and businesses are showcasing more types of lenses and hardware through the marketplace. There are five significant components of AR:
Artificial intelligence. Most augmented reality solutions need artificial intelligence (AI) to work, allowing users to complete actions using voice prompts. AI can also help process information for your AR application.
AR software. These are the tools and applications used to access AR. Some businesses can create their own form of AR software.
Processing. You’ll need processing power for your AR technology to work, generally by leveraging your device’s internal operating system.
Lenses. You’ll need a lens or image platform to view your content or images. The better quality your screen is, the more realistic your image will appear.
Sensors. AR systems need to digest data about their environment to align the real and digital worlds. When your camera captures information, it sends it through software for processing.
Dev Tools for Augmented Reality
ARCore

ARCore is Google’s platform for building augmented reality experiences. Using different APIs, ARCore enables your phone to sense its environment, understand the world and interact with information. Some of the APIs are available across Android and iOS to enable shared AR experiences.
echo3D

echo3D is a cloud platform for 3D/AR/VR/Spatial Computing content management and distribution that provides tools and network infrastructure to help developers & companies build and deploy 3D apps, games, and content.
Vuforia

Vuforia is a software development kit (SDK) which is a collection of software tools, libraries, and documentation that enables developers to build applications for specific platforms. It can be used to build augmented reality apps for mobile devices.
Vuforia is not a standalone tool but is rather dependent on other tools like the Unity game engine. Unity is a cross-platform game engine developed by Unity Technologies to facilitate the creation of game development, virtual reality applications, and even train Artificial Intelligence (AI) models.
Spark AR Studio

Spark AR Studio is an augmented reality platform for Mac & Windows that allows you to somewhat easily create AR effects for mobile cameras. Think of it like Photoshop or Sketch but for AR. Basically, Spark AR is a Facebook studio tool that allows users to build their own virtual and augmented reality effects.
Uses of Augmented Reality

AR can be used in the following ways:
Retail. Consumers can use a store's online app to see how products, such as furniture, will look in their own homes before buying.
Entertainment and gaming. AR can be used to overlay a virtual game in the real world or enable users to animate their faces in different and creative ways on social media.
Navigation. AR can be used to overlay a route to the user's destination over a live view of a road. AR used for navigation can also display information about local businesses in the user's immediate surroundings.
Tools and measurement. Mobile devices can use AR to measure different 3D points in the user's environment.
Architecture. AR can help architects visualize a building project.
Military. Data can be displayed on a vehicle's windshield that indicates destination directions, distances, weather and road conditions.
Archaeology. AR has aided archaeological research by helping archeologists reconstruct sites. 3D models help museum visitors and future archeologists experience an excavation site as if they were there.
Major Challenges
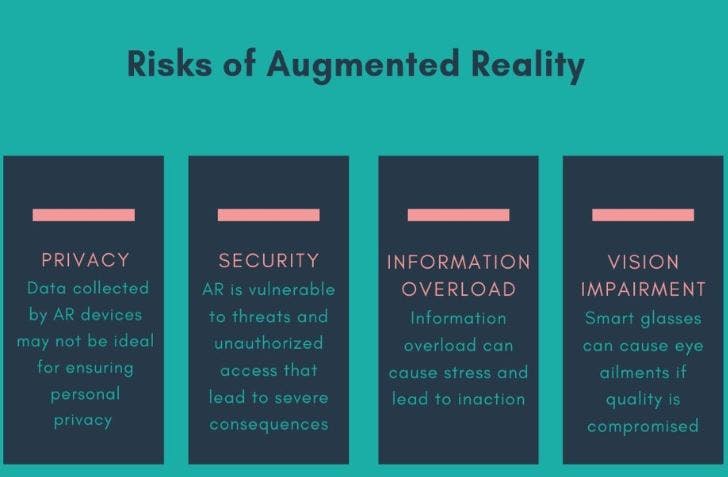
Lack of Proven Business Models. ...
Lack of Augmented Reality App Design & Development Standards. ...
Security & Privacy Issues with Augmented Reality. ...
The Possibility of Physical Harm. ...
Poor Quality of Content & Use Cases. ...
Social Issues of Augmented Reality: Public Acceptance & Retention.
IMPLEMENTATION COST
The Future of AR

As technology continues to evolve at an astounding rate, the possibilities for AR seem limitless. We can expect to witness advancements in AR hardware, with sleeker and more powerful devices that seamlessly integrate into our daily lives. Imagine a future where augmented reality is seamlessly integrated into our homes, workplaces, and even outdoor spaces, enhancing our reality in ways we never thought possible. As these technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and transformative uses in the years to come.
Reference
🚩 https://youtu.be/WzfDo2Wpxks?si=UlXNDrb-LG1v694o
🚩 https://youtu.be/XLP4YTpUpBI?si=uXhwotm3Qi0DeOzN
🚩 https://dynamics.microsoft.com/en-in/mixed-reality/guides/what-is-augmented-reality-ar/
That's all for this blog, I hope you will learn something new. And feel free to share your thoughts and feedback, Thanks for reading.
Feel free to reach out to me 👀
Twitter 🖱
LinkedIn 🖱
Github 🖱